A Guide to Common Chicken Illnesses
Chickens are charming and hardworking members of the backyard flock, providing us with fresh eggs and endless entertainment. However, just like any other living being, chickens are susceptible to various illnesses that can affect their well-being. In this blog post, we'll explore some common chicken illnesses, their symptoms, and what you can do to keep your feathered friends healthy.
Respiratory Infections
Respiratory infections, such as Infectious Bronchitis (IB) and Mycoplasma gallisepticum, can make chickens feel under the weather. If your feathered friends start coughing, sneezing, or have a runny nose, it might be a sign of a respiratory infection. To tackle this, provide a well-ventilated and clean living space for your chickens. Good hygiene is key to preventing the spread of these illnesses. If symptoms persist, consult with a veterinarian, who may recommend appropriate antibiotics or supportive care to help your chickens breathe easily.

Additionally, consider isolating sick chickens to prevent the illness from spreading to the rest of the flock. Boosting their immune systems with a balanced diet and ensuring they have access to clean water are simple yet effective measures. Vaccination against specific respiratory diseases can be a proactive step to keep your chickens healthy.
Coccidiosis
Coccidiosis, caused by various species of the protozoa Eimeria, is a pesky parasitic disease affecting the intestinal tract of chickens. Diarrhea, weight loss, and lethargy are common signs. To combat coccidiosis, focus on maintaining a clean and dry coop environment. Regularly clean bedding and provide a balanced and nutritious diet to keep your chickens robust and less susceptible to protozoa.

There are coccidiosis preventive medications and vaccines available. Consult your veterinarian to determine the most suitable prevention strategy for your flock. If you suspect coccidiosis, isolate the affected chickens and provide them with supportive care. Prompt action and preventive measures are crucial in managing and preventing the spread of this intestinal ailment among your flock. Regular monitoring and proactive steps will ensure your chickens stay healthy.
Marek's Disease
Marek's Disease primarily targets young chickens, causing tumors, paralysis, and sometimes even fatalities. Vaccination is a vital preventive measure, ideally administered when the chicks are one day old. This vaccine plays a crucial role in safeguarding your flock from the devastating effects of Marek's Disease. Regular health checks are essential, allowing you to detect any early signs of the disease. If you notice symptoms like unexplained weight loss or paralysis, seek prompt veterinary assistance.

Unfortunately, there's no cure for Marek's Disease, so early detection and prevention through vaccination are key to protecting your chickens.
Fowl Pox
Fowl Pox is a viral disease recognizable by the development of pox-like lesions on the skin and mucous membranes of chickens. While the illness is usually self-limiting, severe cases can affect the respiratory system. Good hygiene practices, including maintaining a clean coop and minimizing exposure to mosquitoes, can help prevent Fowl Pox. If your chickens show signs of the disease, isolate the affected ones and provide supportive care. Regularly disinfecting the coop and applying antiseptic ointments to lesions can aid in their recovery.
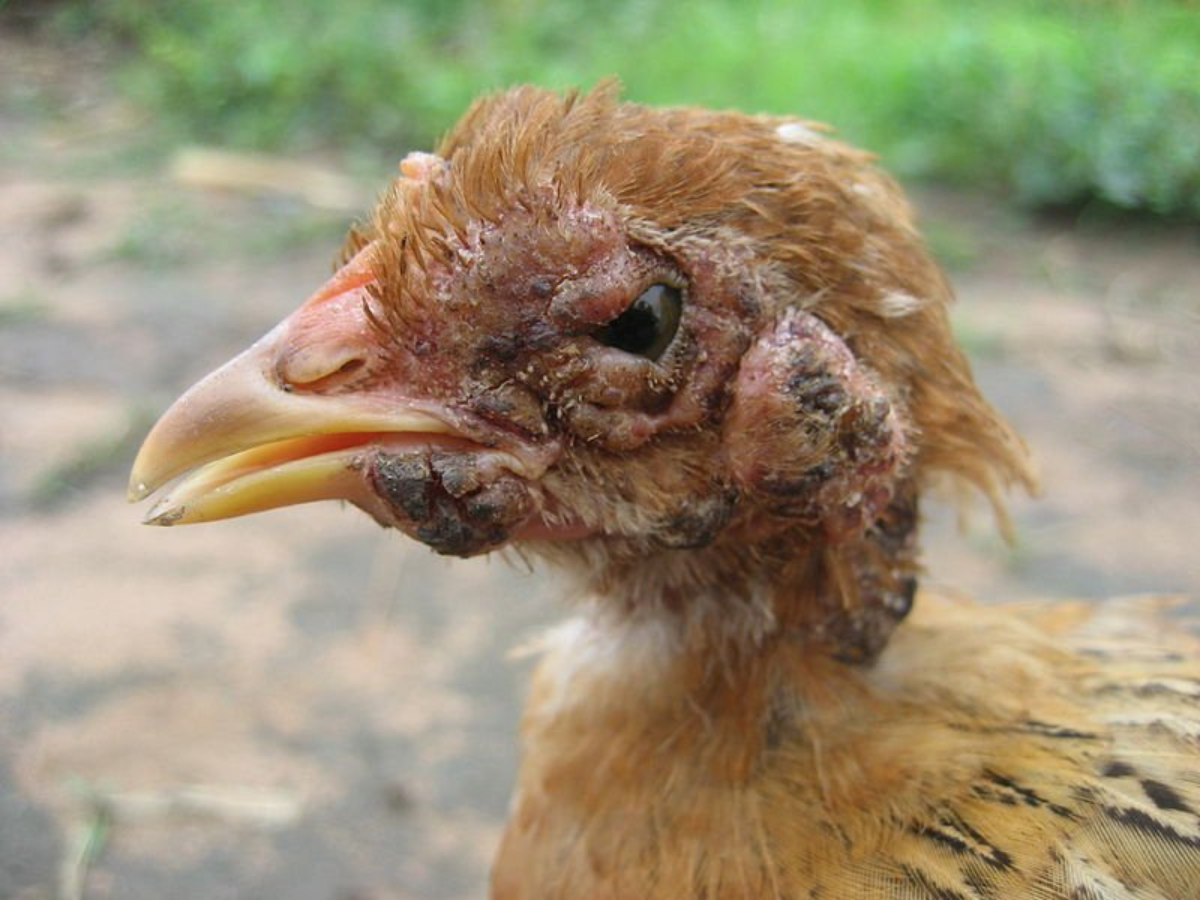

Consult with a veterinarian to discuss vaccination options for preventing Fowl Pox in your flock.
Newcastle Disease
Newcastle disease is highly contagious, affecting the respiratory, nervous, and digestive systems of chickens. If you observe respiratory distress, nervous signs, or a sudden drop in egg production, consult with a vet promptly. Vaccination is a critical preventive measure to protect your flock from Newcastle disease. Additionally, practice strict biosecurity measures to avoid introducing the virus to your premises.

Quarantine new birds before introducing them to the flock, and limit contact with wild birds. Swift action and preventive measures are key to managing and preventing the spread of this serious disease.
Avian Influenza (Bird Flu)
Avian influenza is a viral infection with potential zoonotic implications. If your chickens exhibit severe respiratory distress, head swelling, or a sudden decrease in egg production, contact a veterinarian immediately. Biosecurity measures are crucial to preventing the introduction of the virus to your flock. Restrict access to your coop and run, and avoid contact with wild birds. In areas where avian influenza is prevalent, follow government guidelines and recommendations. Vigilance, prompt reporting of any suspicious symptoms, and adherence to biosecurity measures are essential to protecting both your flock and human health.
Salmonella
Chickens can carry and transmit Salmonella, which can lead to symptoms like diarrhea and lethargy. To prevent Salmonella, practice good hygiene in handling eggs and cleaning the coop regularly. Provide clean water and a balanced diet to maintain the overall health of your flock. If you suspect Salmonella, isolate the affected chickens, and consult with a veterinarian. Antibiotics may be prescribed, and supportive care is crucial for recovery.

Remember, Salmonella is a concern not only for chickens but also for human health. Wash your hands thoroughly after handling chickens or their eggs to reduce the risk of transmission.
Internal Parasites
Worms such as roundworms, tapeworms, and cecal worms can negatively impact chickens' health. To prevent internal parasites, practice regular deworming based on veterinary recommendations. Keep the coop and run clean, as cleanliness plays a crucial role in minimizing the risk of worm infestations. Provide a balanced diet to ensure your chickens are healthy and resilient.

If you notice signs of worm infestation, such as poor growth or weight loss, consult with a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
External Parasites
Mites and lice can be a nuisance for chickens, causing irritation, feather loss, and even anemia in severe cases. Regularly inspect your flock for signs of external parasites, especially in the warmer months. Implement preventive measures such as dust baths with diatomaceous earth and using poultry-safe insecticides. Keep the coop and nesting areas clean, as these parasites thrive in dirty environments. If an infestation is suspected, isolate the affected birds and treat them promptly with veterinary-approved solutions.
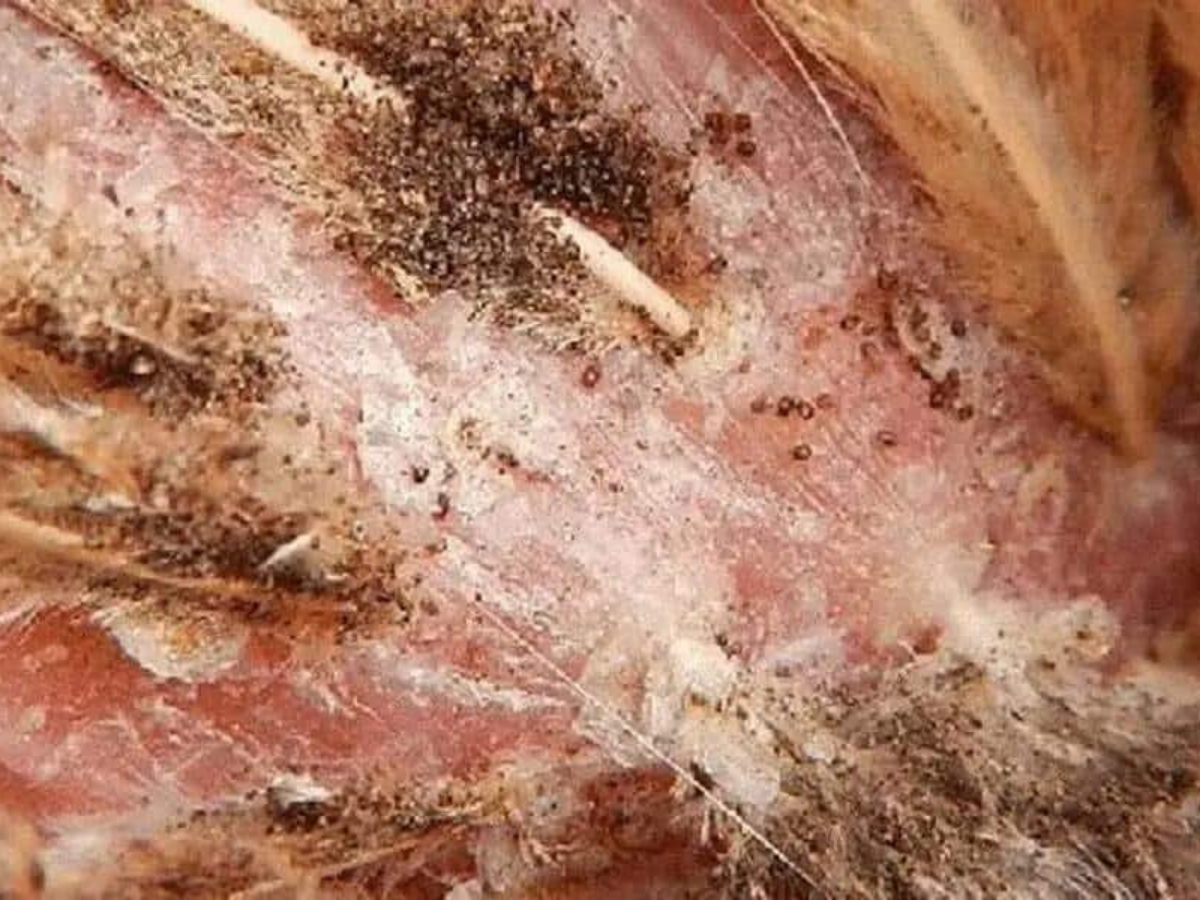
Prevention and early intervention are key to managing external parasites and ensuring the well-being of your flock.
Egg-laying Issues
Problems related to egg-laying, such as egg binding or egg-related peritonitis, can affect the reproductive health of chickens. Provide a comfortable and stress-free nesting environment to encourage normal egg-laying behavior. If you notice signs of distress, lethargy, or abdominal swelling, consult with a veterinarian. In some cases, gentle massage and warm baths may help alleviate egg-binding. However, professional veterinary advice is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
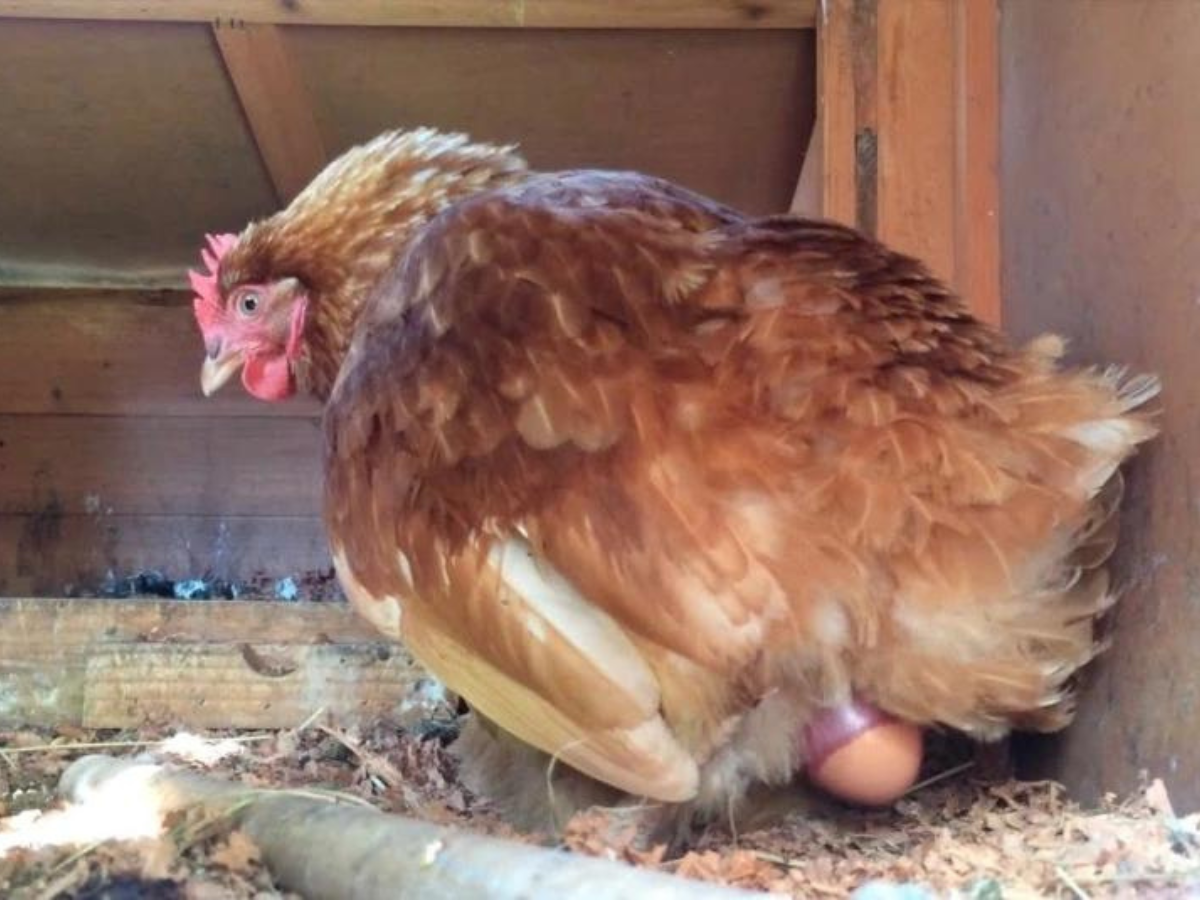

Regularly check for abnormalities in egg production and seek assistance if you notice any irregularities. Ensuring optimal conditions for egg-laying can contribute to the overall health and happiness of your flock.
Conclusion
Keeping your chickens healthy involves a combination of proper care, hygiene, and being vigilant for any signs of illness. Regular health checks and prompt action can go a long way in ensuring a happy and thriving flock. After all, healthy chickens lay the best eggs!
